why does dka cause metabolic acidosis Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Welcome, health enthusiasts! Today, we are going to dive deep into the fascinating world of anion gap metabolic acidosis. This is an essential topic to understand when it comes to diagnosing and treating certain medical conditions. So, let’s get started and explore this intriguing issue together!
Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis
 What exactly is anion gap metabolic acidosis, you may ask? Well, it is a condition where there is an increase in the concentration of acid in the body. This occurs due to the accumulation of acidic molecules, resulting in an imbalance in the body’s pH levels.
What exactly is anion gap metabolic acidosis, you may ask? Well, it is a condition where there is an increase in the concentration of acid in the body. This occurs due to the accumulation of acidic molecules, resulting in an imbalance in the body’s pH levels.
There are various causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, and ingestion of toxic substances. It is important to identify the underlying cause to provide appropriate treatment.
One way to differentiate between different types of acidosis is by assessing the anion gap, which can be calculated using the formula:
Anion Gap = (Na+) - (Cl- + HCO3-)
Now, let’s take a moment to understand the significance of this formula. By measuring the anion gap, healthcare professionals can determine the cause of metabolic acidosis. If the anion gap is elevated, it suggests the presence of other acidic substances in the body.
Understanding Acidosis vs. Alkalosis
 To fully comprehend anion gap metabolic acidosis, it is crucial to differentiate it from other acid-base imbalances, such as alkalosis. Acidosis refers to a condition where the body’s pH falls below the normal range, indicating the presence of excess acid. On the other hand, alkalosis occurs when the body’s pH rises above the normal range, suggesting a higher alkaline state.
To fully comprehend anion gap metabolic acidosis, it is crucial to differentiate it from other acid-base imbalances, such as alkalosis. Acidosis refers to a condition where the body’s pH falls below the normal range, indicating the presence of excess acid. On the other hand, alkalosis occurs when the body’s pH rises above the normal range, suggesting a higher alkaline state.
In the case of anion gap metabolic acidosis, the body becomes more acidic due to the increased production or accumulation of acid. This disrupts the delicate balance required for optimal bodily function.
Treating anion gap metabolic acidosis involves targeting the underlying cause. For example, if it is caused by diabetic ketoacidosis, insulin therapy and fluid resuscitation are essential components of treatment. Additionally, close monitoring of electrolyte levels is crucial to achieve a balanced pH level.
Remember, if you suspect any symptoms of anion gap metabolic acidosis, such as rapid breathing, confusion, or lethargy, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and ensuring a speedy recovery.
In conclusion, anion gap metabolic acidosis is a complex medical condition that requires careful evaluation and prompt treatment. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and causes, healthcare professionals can provide effective care to patients. So, stay informed and spread the knowledge to help create a healthier world!
If you are looking for Dx Schema – Anion gap metabolic acidosis – The Clinical Problem Solvers you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Dx Schema – Anion gap metabolic acidosis – The Clinical Problem Solvers like Respiratory/Metabolic Acidosis vs. Alkalosis https://www.facebook.com, ข่าวสารสัตว์ปีก: กรดใน GI ทำให้เกิด Metabolic acidosis and also Metabolic Acidosis | Nursing mnemonics, Metabolic acidosis, Nursing. Here you go:
Dx Schema – Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis – The Clinical Problem Solvers
 clinicalproblemsolving.comacidosis gap anion metabolic solvers clinicalproblemsolving
clinicalproblemsolving.comacidosis gap anion metabolic solvers clinicalproblemsolving
Metabolic Acidosis | Nursing Mnemonics, Metabolic Acidosis, Nursing
 www.pinterest.co.krmetabolic acidosis alkalosis mnemonics hyperkalemia electrolytes tachypnea signs diarrhea respiratory rn base asidosis ketoacidosis renal failure starvation hypovolemic acute interventions
www.pinterest.co.krmetabolic acidosis alkalosis mnemonics hyperkalemia electrolytes tachypnea signs diarrhea respiratory rn base asidosis ketoacidosis renal failure starvation hypovolemic acute interventions
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
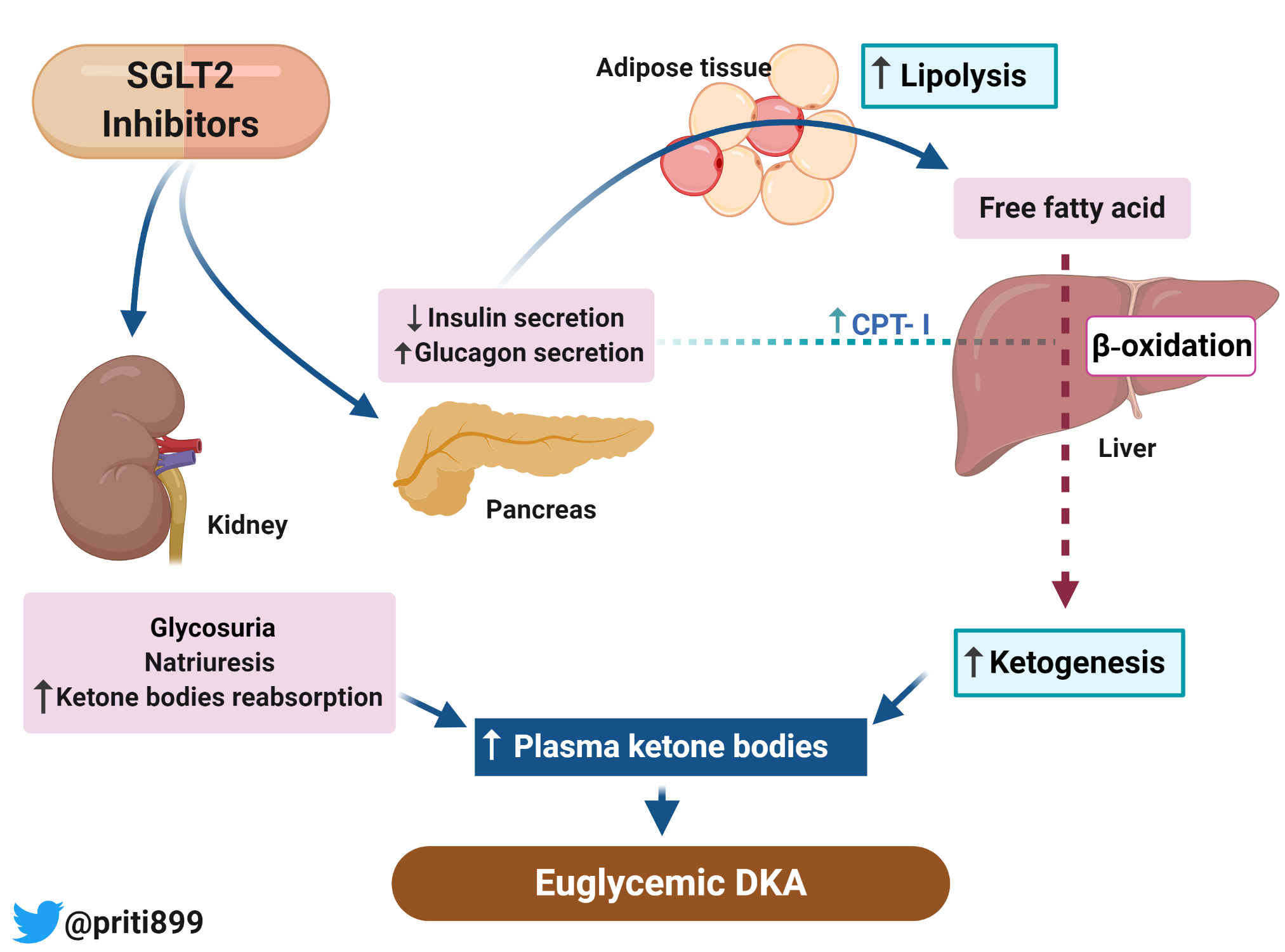 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria principles transplantation immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Respiratory/Metabolic Acidosis Vs. Alkalosis Https://www.facebook.com
 www.pinterest.comacidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico
www.pinterest.comacidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico
ข่าวสารสัตว์ปีก: กรดใน GI ทำให้เกิด Metabolic Acidosis
 thaiavian.blogspot.comSglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Acidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico. ข่าวสารสัตว์ปีก: กรดใน gi ทำให้เกิด metabolic acidosis
thaiavian.blogspot.comSglt2 inhibitor-induced euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. Acidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico. ข่าวสารสัตว์ปีก: กรดใน gi ทำให้เกิด metabolic acidosis