fehling test for aldehyde and ketone Fehling fehlings principle interpretation
A professional in the field of chemistry understands the importance of various chemical tests in determining the presence of specific compounds. One such test is Fehling’s Test, which is commonly used to detect the presence of aldehydes and ketones. This test relies on the redox reaction between the carbonyl compound and the Fehling’s solution. Let’s delve deeper into the principle, procedure, results, and uses of this important chemical test.
Fehling’s Test: Definition
Fehling’s Test is a chemical test used to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. It is based on the ability of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones to undergo oxidation under alkaline conditions. This test was first developed by German chemist Hermann Von Fehling in the mid-19th century, hence the name.
Principle of Fehling’s Test
The principle behind Fehling’s Test lies in the redox reaction that takes place between the carbonyl group of the aldehyde or ketone and the Fehling’s solution. The Fehling’s solution consists of two separate solutions: Fehling’s A (copper(II) sulfate) and Fehling’s B (an alkaline solution of sodium potassium tartrate). When Fehling’s A and B are mixed in equal proportions, an intense blue-colored solution is formed due to the presence of copper(II) ions.
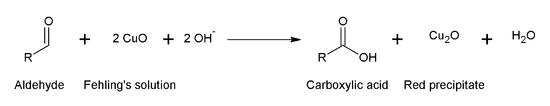 When a reducing sugar (an aldehyde or a ketone) is added to the Fehling’s solution and heated, it undergoes oxidation. The aldehyde present in the reducing sugar reduces the copper(II) ions in Fehling’s solution to copper(I) ions, which results in the formation of a reddish-brown precipitate of copper(I) oxide. This clearly indicates a positive Fehling’s Test.
When a reducing sugar (an aldehyde or a ketone) is added to the Fehling’s solution and heated, it undergoes oxidation. The aldehyde present in the reducing sugar reduces the copper(II) ions in Fehling’s solution to copper(I) ions, which results in the formation of a reddish-brown precipitate of copper(I) oxide. This clearly indicates a positive Fehling’s Test.
Procedure of Fehling’s Test
The procedure for conducting Fehling’s Test involves a series of meticulous steps:
- Take Fehling’s A and Fehling’s B solutions in equal volumes and mix them together.
- Add a small quantity of the substance to be tested (aldehyde or ketone) to the Fehling’s solution.
- Heat the mixture in a boiling water bath or using a Bunsen burner flame.
- Observe the color change and the formation of any precipitate.
The presence of a brick-red precipitate indicates a positive result, suggesting the presence of reducing sugars such as aldehydes or ketones.
Results and Interpretation
The interpretation of Fehling’s Test results depends on the appearance of colors and precipitates:
- Positive Test: When a brick-red precipitate is formed, it indicates the presence of aldehydes or ketones. The darker the precipitate, the greater the amount of the reducing sugar present.
- Negative Test: If no precipitate is formed and the solution remains blue, it indicates the absence of aldehydes or ketones.
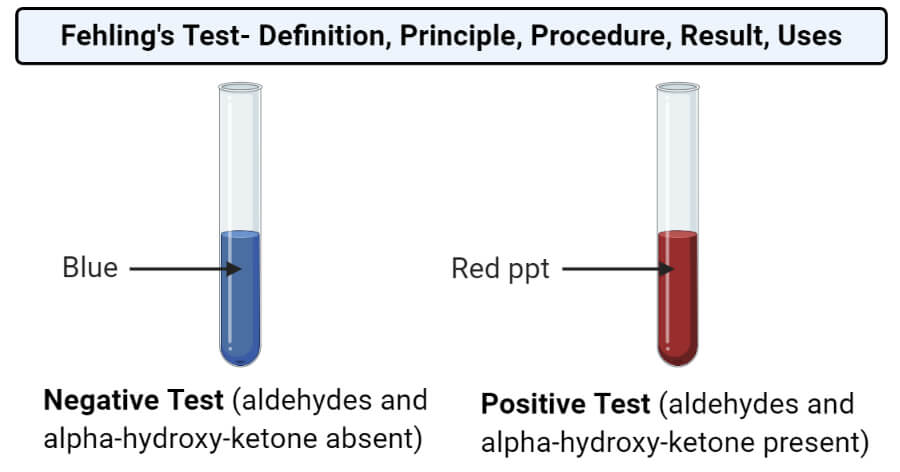 The color change in the Fehling’s solution from intense blue to brick-red precipitate provides a clear visual indication of the presence or absence of aldehydes or ketones.
The color change in the Fehling’s solution from intense blue to brick-red precipitate provides a clear visual indication of the presence or absence of aldehydes or ketones.
Uses of Fehling’s Test
Fehling’s Test finds its applications in diverse areas:
- Qualitative Analysis: Fehling’s Test is extensively used in the laboratory to differentiate between aldehydes and ketones. This helps chemists identify and characterize organic compounds.
- Food Industry: Fehling’s Test is employed in the food industry to detect reducing sugars present in various food products. It helps determine the purity of sugar, honey, and other sweetening agents.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Fehling’s Test is utilized during the synthesis of pharmaceutical drugs to identify and monitor the progress of key chemical reactions.
Fehling’s Test is a well-established and widely used method for the detection of aldehydes and ketones. Its simplicity, speed, and effectiveness make it an indispensable tool in various scientific disciplines. By performing this test, chemists can gain valuable insights into the composition and properties of different compounds, ensuring the advancement of knowledge and innovation in the field of chemistry.
If you are looking for aldehyde-ketone you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about aldehyde-ketone like Fehlings Solution, Ma Chemistry: Aldehyde and Ketone and also Fehling’s Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses. Read more:
Aldehyde-ketone
 majorchemspa.wordpress.comketone aldehyde fehling reagent ปฏ ของ เป แอล กอ ฮอ ล ยา ตภ ผล ได ณ ฑ โดย และ
majorchemspa.wordpress.comketone aldehyde fehling reagent ปฏ ของ เป แอล กอ ฮอ ล ยา ตภ ผล ได ณ ฑ โดย และ
Ma Chemistry: Aldehyde And Ketone
 d-dream-halfblood.blogspot.comketone aldehyde fehling reagent ปฏ ของ แอล กอ ฮอ ล ได ผล ตภ ณ ฑ ยา reduction โดย chemistry
d-dream-halfblood.blogspot.comketone aldehyde fehling reagent ปฏ ของ แอล กอ ฮอ ล ได ผล ตภ ณ ฑ ยา reduction โดย chemistry
Tests For Aldehydes And Ketones - Sodium Bisulphite(NaHSO3), 2,4
 byjus.comketones aldehydes tests chemistry test procedure organic compound given solution ethanol setup
byjus.comketones aldehydes tests chemistry test procedure organic compound given solution ethanol setup
Fehlings Solution
 byjus.comtest fehling solution fehlings
byjus.comtest fehling solution fehlings
Fehling’s Test- Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
 microbenotes.comfehling fehlings principle interpretation
microbenotes.comfehling fehlings principle interpretation
Tests for aldehydes and ketones. Ketone aldehyde fehling reagent ปฏ ของ เป แอล กอ ฮอ ล ยา ตภ ผล ได ณ ฑ โดย และ. Fehlings solution